Top Cybersecurity Strategies to Protect Your Business Website in 2025
In 2025, it’s time to look at more than just basic security for protecting your online business from possible threats. When the threats have taken on a more significant role, it becomes apparent that expending resources on cybersecurity should take an even higher position on your priority list. The article will provide top cybersecurity strategies that would protect your business website.
- May 22, 2025
- by Tarun


The digital landscape is seeing rapid changes and creating new challenges and opportunities for businesses across the globe. Given the growing dependence on the online medium, securing your business website is more important than ever. Cyber threats are getting sophisticated, exploiting the inefficiencies of technology as well as human behavior. Ransomware as a service attack, data breaches typical to the market, and AI-targeted exploits—these virtually every kind of risk is real and posed against your business.
Thus, there will be a need to have in place cybersecurity strategies that are robust enough to guard against these threats, but also flexible enough to foresee emerging threats-and in fact, there exists a market for such consultation. This article explores some of the top cybersecurity strategies that every business should engage in 2025 to secure its websites and the trust of its client.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
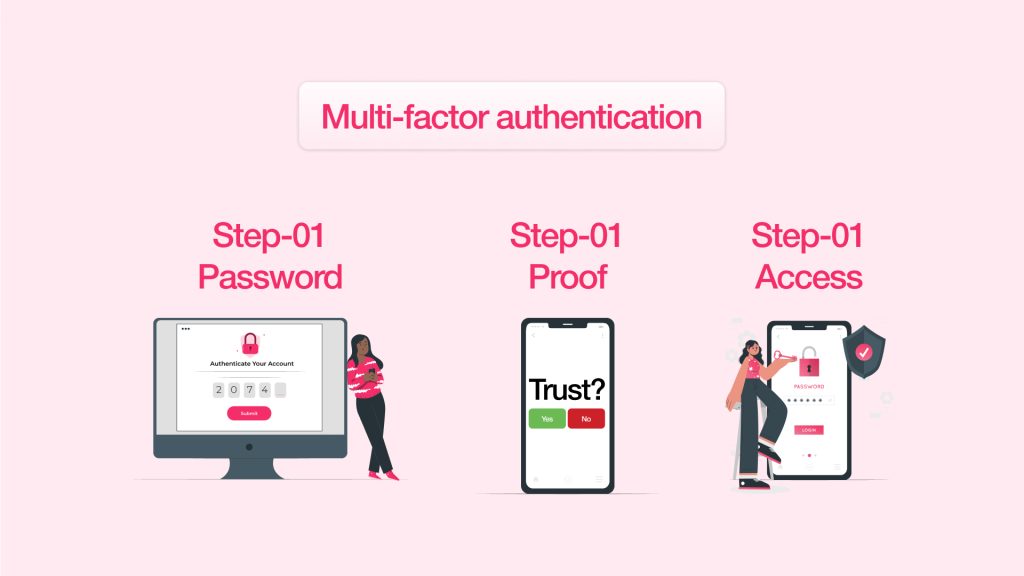
Multi-Factor authentication adds an additional layer of security where users must provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a resource. These factors may include something known (like a password), something possessed (like a smartphone) or something that identifies when the person is identified (like a fingerprint).
For example, imagine you’re logging into your company’s email system. With MFA, you will receive a code after you enter your password and before completing the login. This improves security by requiring verification through another means (the code) even if a hacker learns that password.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Performing a regular security audit and penetration test is fundamental to identifying any vulnerabilities in your system. Security Audit refers to a comprehensive inspection of all your organization’s cybersecurity policies, procedures, and controls; and Penetration Testing consists of artificially recreating real-world attacks to put your defenses through their paces.
Think of it like a health check-up for your cybersecurity. You might find that some areas are in good shape, while others need immediate attention. By addressing those weaknesses proactively, we can greatly minimize the chances of a breach.
Employee Training and Awareness Program
Employees prove to be the first line of defense against cyber threats. Yet they can act as the most disadvantaged link in the chain when not properly trained. Employee training and awareness programs are vital for educating your staff on best practices and lay of bad threats.
As an example, phishing emails are a popular means to try and trick employees into revealing sensitive information. It is possible to prevent breaches by teaching employees to recognize and report phishing emails. Sign up for regular training sessions, conduct mock phishing attempts, and develop clear guidelines.
Strong Password Policies
Weak passwords are the easiest targets for breaking into any system. Developing a sound password policy would drop this risk down to size. They must use complex passwords, mix uppercase and lowercase letters with numbers and special characters, as much as possible.
Also, try using password managers to manage strong passwords. They generate and keep strong passwords but may also warn about weak or re-used passwords, potentially improving overall security efforts.
Data Encryption
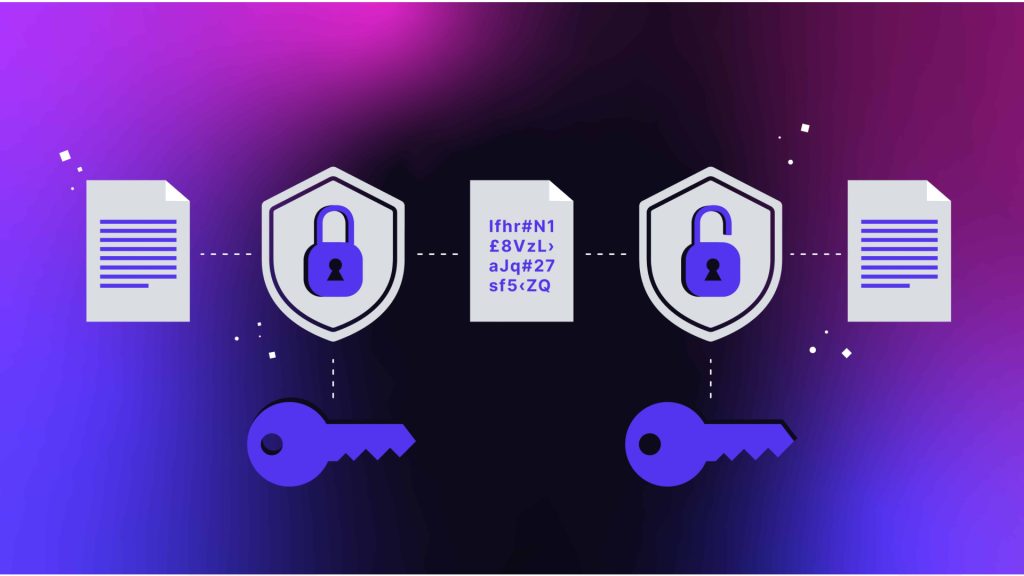
Data encryption is a basic cybersecurity strategy that ensures data protection while the information is in storage and transit. Essentially, encryption changes readable data into something unreadable so that anyone who intercepts data without the decryption key will find it useless.
For example, if your organization holds sensitive customer information, encryption means even if a hacker manages to gain access to your systems, they cannot read or use that information.
Regular Software Updates and Patch Management
Outdated software is the most common approach for cyber-attacks. Regular software updates and patch management is a way to seal up all vulnerabilities exploited by known vulnerabilities. Many companies fall far behind on updates owing to some bothered situations, but the risk of not updating is far high.
Automating this update process will ensure that all systems are informed of these changes without any need for manual intervention. Further, a policy on patch management will free up time in planning making critical updates.
Need a reliable software maintenance and updates partner to help grow your business?
Our Experts Can Help!
Network Segmentation
Network Segmentation refers to breaking down the whole network into smaller segments with lower visibility to each other. This may help in limiting the spread of the attack and minimize the attack damage. In case one of the segments gets compromised, the other segments are still secured.
It means that if a company has an HR department, a finance department, and an IT department, then the HR segment can be tied to a network segment by itself; should a breach occur in that area, it will not affect the other segments.
Incident Response Plan
Despite the strength of your cybersecurity defenses, you must always have a good incident response plan. Such a plan provides instructions on how to detect, respond to, and recover from a breach.
A well-prepared incident response plan should incorporate detailed roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and a recovery process. The plan should also be periodically tested using various simulations, to ensure that everyone knows the actions to take during a real emergency.
Use Advance Threat Modelling Tools
Advanced threat detection tools analyze network behavior, user activity, and system processes to spot anomalies that might indicate an attack. Threat detection is usually realized by systems with artificial intelligence and machine learning, which speed up and reduce threat-detection time.
For instance, if an employee suddenly begins transferring large amounts of data after hours, threat detection systems would flag that for immediate attention. Tools like EDR, XDR, SIEM, etc., form the backbone of modern-day infrastructure for cybersecurity.
Secure Website Architecture and Design
It is said that a secure website is built on secure ground; hence, it becomes an easy target for cybercriminals if a website is badly designed, contains outdated code, or uses vulnerable frameworks.
Some secure development practices that should be followed by businesses include:
- Input validation to prevent injection attacks.
- Accessing HTTPS and using secure cookies.
- Minimizing backend information exposure.
- Removing all unnecessary plug-ins and services.
Regular code reviews and automated scanning tools help point out weaknesses and remedies with minimal timing to reduce the attack surface.
Need a Stunning Web Design Services?
We Can Help!
Web Application Firewalls (WAFs)
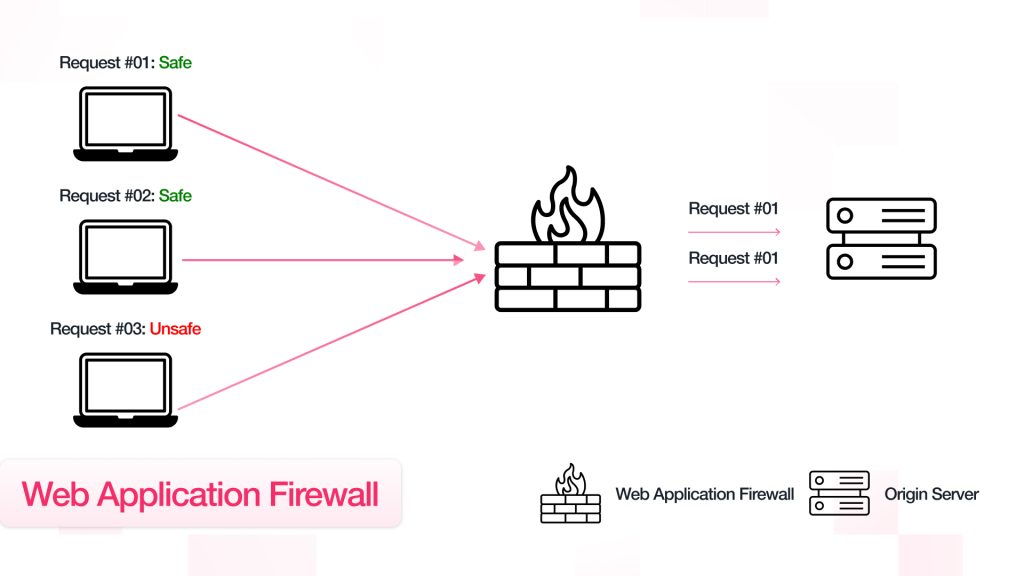
WAFs basically work like a firewall, except that they pay closer attention to incoming HTTP requests from visitors to the site. They monitor, scrutinize, and block any malicious requests from these visitors in an attempt to prevent attacks like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and denial of service.
In 2025, increased dependency on cloud service and API integration will push WAFs into a new direction; adapting to current demands for cloud compatibility. Selecting one of those reputable WAFs proves critical in protection effectiveness, bringing along both real-time analytics and threat intelligence, along with customizable rule sets.
Secure API Management
APIs are often overlooked for security risks, yet they are frequently attacked by potential attackers. Insecure APIs may give access to sensitive data and act as gateways into critical systems.
To secure APIs:
- Use authentication and authorization mechanisms like OAuth2.0
- Enforce rate-limiting to ward off abuse
- Audit and monitor API traffic on a regular basis
- Discourage exposing endpoints that are not really needed
An inventory of APIs with good documentation helps maintain visibility and thus lowers the chance for “shadow” APIs to go unmonitored and unprotected.
Cloud Security Best Practices
With more and more businesses switching to the clouds, securing cloud environments has become a priority. Misconfigured clouds and cloud storage loudly claim their share as one of the top reasons for a breach of data.
Effective cloud security includes:
- Implementing least privilege for access control
- Encryption in transit and at rest
- Logging and monitoring must be enabled
- Establishing secure backups and disaster recovery procedures
Regardless of companies using the AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud environment, they should align their practices with that respective platform’s security recommendations and standards.
Domain and DNS Protection
Cyber criminals use the DNS system as a means to reroute traffic, hijack domains, or launch phishing attacks. A hacked DNS can quietly redirect users to unsafe sites.
To prevent this use:
- DNS Security Extensions, or DNSSEC
- Register domains with trusted registrars
- Activate a domain lock to prevent unauthorized transfer
- Keep monitoring domain records for suspicious changes
In these ways, you will ensure that the traffic to your website is secured and thus won’t make your online presence untrustworthy.
Monitor For Credential Leaks
In 2025, credential stuffing continues to remain a large threat due to password reuse. Cybercriminals source their stolen accounts from earlier breaches and try the credentials across different platforms.
While it will not make your organization invincible against attacks from credential stuffing, paying attention to dark web forums or data breach databases to find leaked credentials is a good move to take preventive action before an attacker does. Numerous security platforms offer automated alerts when business credentials are detected in known breaches.
Changed frequently, these passwords should be made the most secure by requiring MFA after each entry.
Secure Remote Access
In modern businesses, hybrid work models are in place, so remote access security is obligatory. Employees usually access internal systems using home Wi-Fi or personal devices, potentially risking company data.
Some of the key strategies include:
- VPN usage
- Device compliance policies enforcement
- Installation of endpoint protection software
- Access control based on user role and health of the device
Remote access policies must be periodically reviewed so that they reflect current usage and threat trends.
Monitor Insider Threats
We cannot forget that not all threats are external. Insider threats, either malicious or accidental, can wreak havoc. One employee might misuse access to sensitive data, while another might be a victim of social engineering or phishing scams, thereby facilitating breaches.
To mitigate this:
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools should be employed.
- Track User Behavior.
- Access Rights must be kept at the least level required for a user to perform the specific job role.
- Customer education about data handling protocols is a must.
Regular audits and implementing a strong security culture goes a long way to minimize risk from within.
Invest in Cybersecurity Insurance
However, as ideal as it may sound, no system is completely safeguarded from a possible cyber-attack. Instead, cybersecurity insurance provides a financial safety net in the event of such a breach. Insurance policies might cover loss of data, business interruption, litigation, and reputation management.
Before selecting its policy, it is important to:
- Determine what insurance coverage is required according to the business model
- Understand the breach response capacity of the insurer
- Understand the terms and exclusions of the policy
This extra layer of protection could provide peace of mind and resources during recovery.
Continuous Improvement and Compliance
Cybersecurity is not a task to finish; rather, it deserves regular focus, adjustment, and learning. Defense needs to evolve with the threat. Compliance with data privacy laws and standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS ensures that the security measures you use are adequately robust and legit.
On a regular basis, testing will inform you on threat intelligence, new technology, and regulations. In fact, cybersecurity should be involved in business planning from the start, as opposed to last-minute consideration.
Conclusion
The way you protect your commercial business website in 2025 must involve proactive measures and a well-defined structure for the resolution of cybersecurity concerns. These strategies outlined in this article-from two-factor authentication to threat detection and cloud security-are intended to mitigate every possible threat present in the business today.
Adopting such strategies will help protect your sensitive data, operational business continuity, and build lasting trust with customers and partners.
Bear in mind that cyber threats aren’t going away but with an effective defense in place, your business should not be an easy target.
 Shopify
Shopify










